Wild animals used for traditional medicine
Every year, thousands of animals are bred in captivity or snatched from the wild to be brutally killed for their body parts.
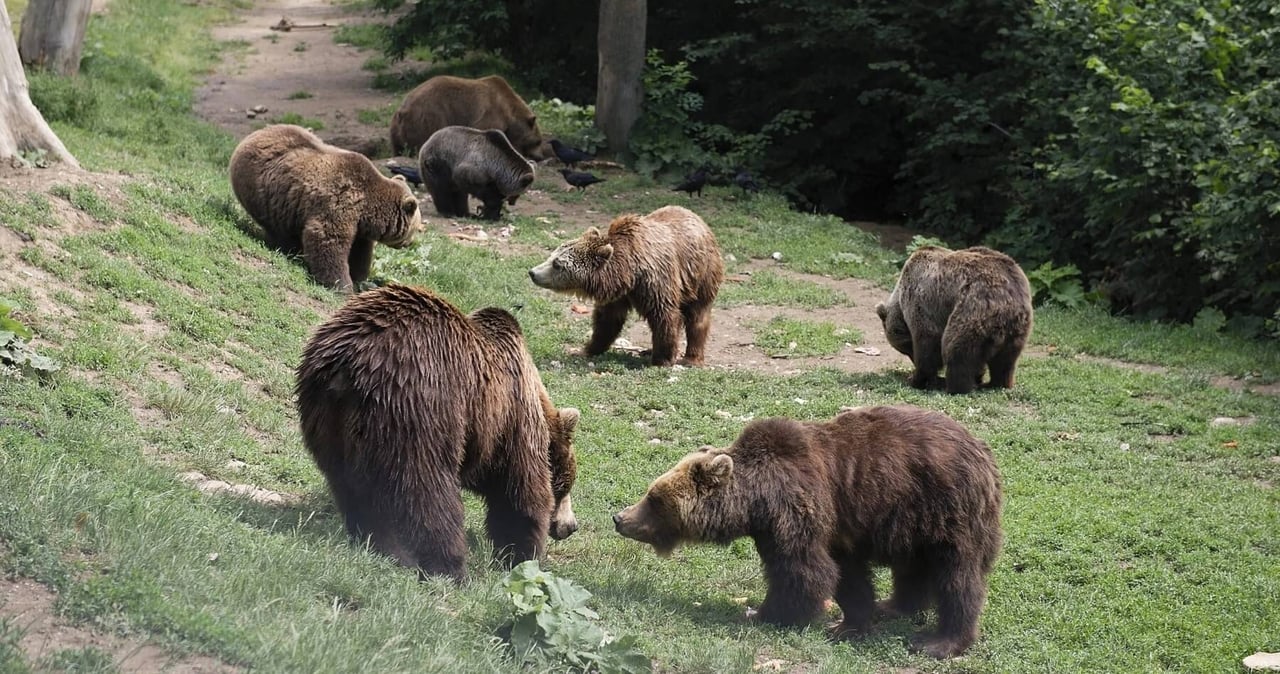

Bears are omnivorous – meaning they eat basically everything – with an excellent sense of smell, even rivalling that of dogs.
Bears are highly intelligent animals. They can count, use tools, solve problems and communicate with a range of vocalisations and complex facial expressions. Bears are typically solitary animals except during mating season and mothers when nursing their young. Despite their size and heavy build, bears are good runners, climbers, and swimmers.
Over the winter, bears dig dens or use shelters such as caves and logs to go into a deep sleep during winter periods, referred to as “torpor”. Contrary to popular belief, bears are not true hibernators.
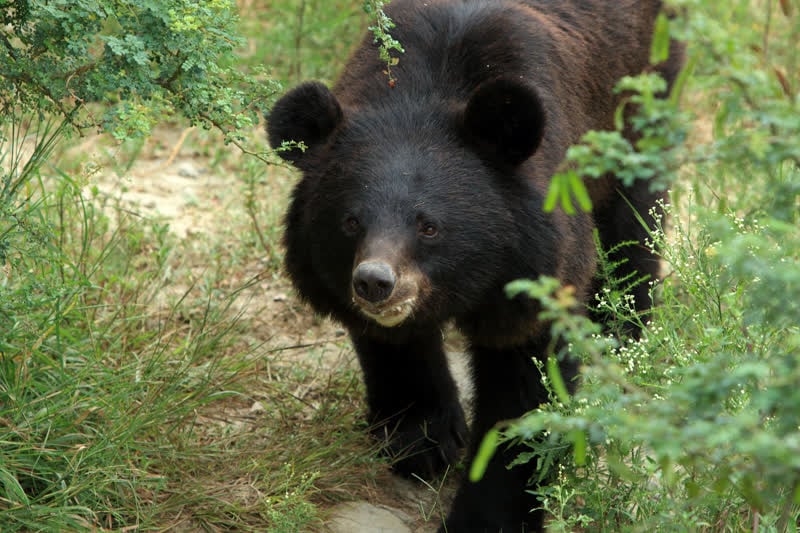


The Asiatic black bear, also called the Asian black bear, or moon bear, is a member of the black bear family. It’s found in the Himalayas, northern parts of the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and parts of eastern Asia including northeastern China, the Korean Peninsula and Japan.
The Asiatic black bear has black fur, a light brown muzzle, and a distinct white patch on the chest, which is sometimes V-shaped.
Asiatic black bears are classed as “vulnerable” to extinction by the IUCN (Red List of Endangered Species); and as Appendix I under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Flora and Fauna (CITES).
Wild populations of Asiatic black bears have been declining by 30% over the last 30 years and are projected to decline by more than 30% over the next 30 years due to hunting and habitat loss.
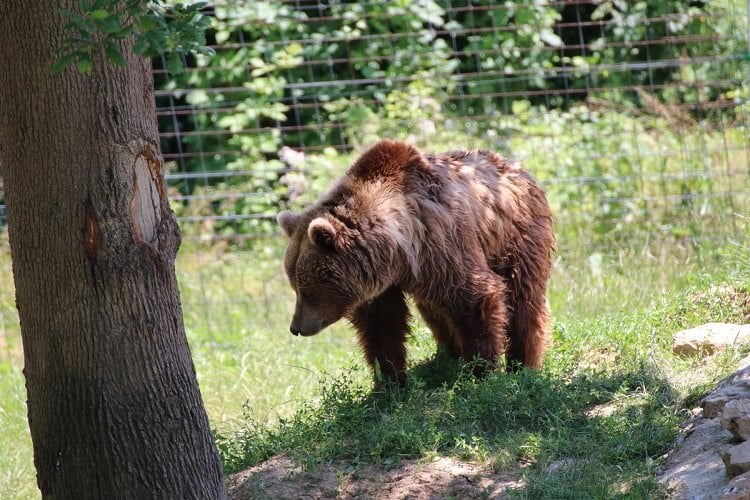
The brown bear is Europe’s largest terrestrial mammal. The total population for continental Europe is estimated at between 10,000 and 11,000 bears.
The species was once distributed across the whole of the European continent, but has long been extinct in most of western Europe and has recently become extinct in a number of other areas.
The European brown bear’s habitat is forest, however large tracts of forested areas are rapidly vanishing. Human settlement and centuries of hunting have already eliminated brown bear populations from 50-75% of their historic range, and continue to deplete remaining populations.

Bile is a fluid secreted by the liver and stored in the gall bladder of all mammals. It is a necessary part of the digestive process. The gallbladder and bile of bears are highly valued for use in traditional Asian medicine.
Extracted bile can be sold ‘fresh’ in small glass vials, dried in an oven to form powders, and/ or mixed with other ingredients to make pills or other products.
Bear bile is extracted in intolerably cruel and inhumane ways, often by people with no veterinary qualifications and little concern for animal protection.
Extracting bile from live bears cause severe distress and pain. Open wounds from extractions can lead to infections, chronic illness and death.
Bears in the bear bile industry often moan and rock due to extreme anxiety. Many have broken teeth from biting on the bars of their cages.
Our researchers identified 32 herbal alternatives to bear bile already included in traditional medicine compendiums.
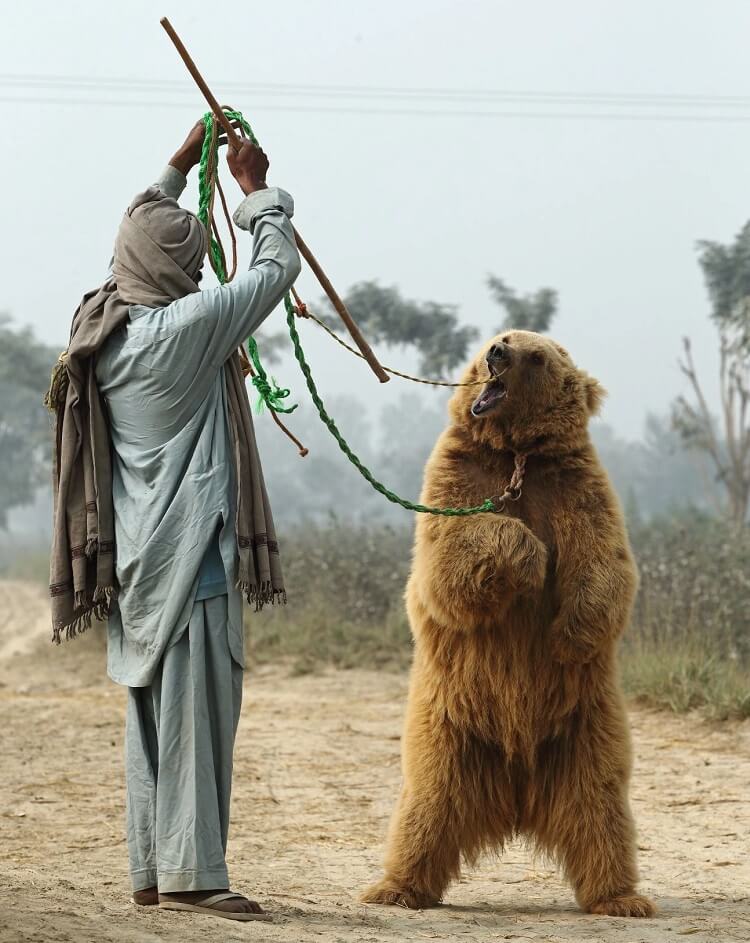
Many bears have been taken from the wild at a very young age, destined for a life of captivity and torture to entertain crowds. To steal the cubs, poachers often shoot the mother bears – depleting the breeding adults and the next generation of wild bears.
In order to train bears to dance, they’re forced to stand on metallic plates heated to unbearable temperatures by hot coals underneath. The trainer controls the heat level and plays a musical instrument to make the bear lift their feet, as if “dancing”, in an attempt to relieve their burning paws. This causes a lifetime of physical and psychological pain. Some dancing bears are offered to baiting event organisers to fight dogs, often influential landlords who own the fighting dogs, – which are seen as status symbols.
At a baiting event, the bear is tied with a neck rope to restrict their movement. This only allows them to rear up and turn around, but not to run or hide. They’ll then be set upon by several dogs at once and have no choice but to try to defend themselves – without sharp teeth or claws. The wounds, terror, and pain inflicted on these bears is horrifying and heartbreaking.
Bears used for bear baiting very rarely make it past the age of eight. When one bear dies, the cycle begins again and another is taken from the wild.


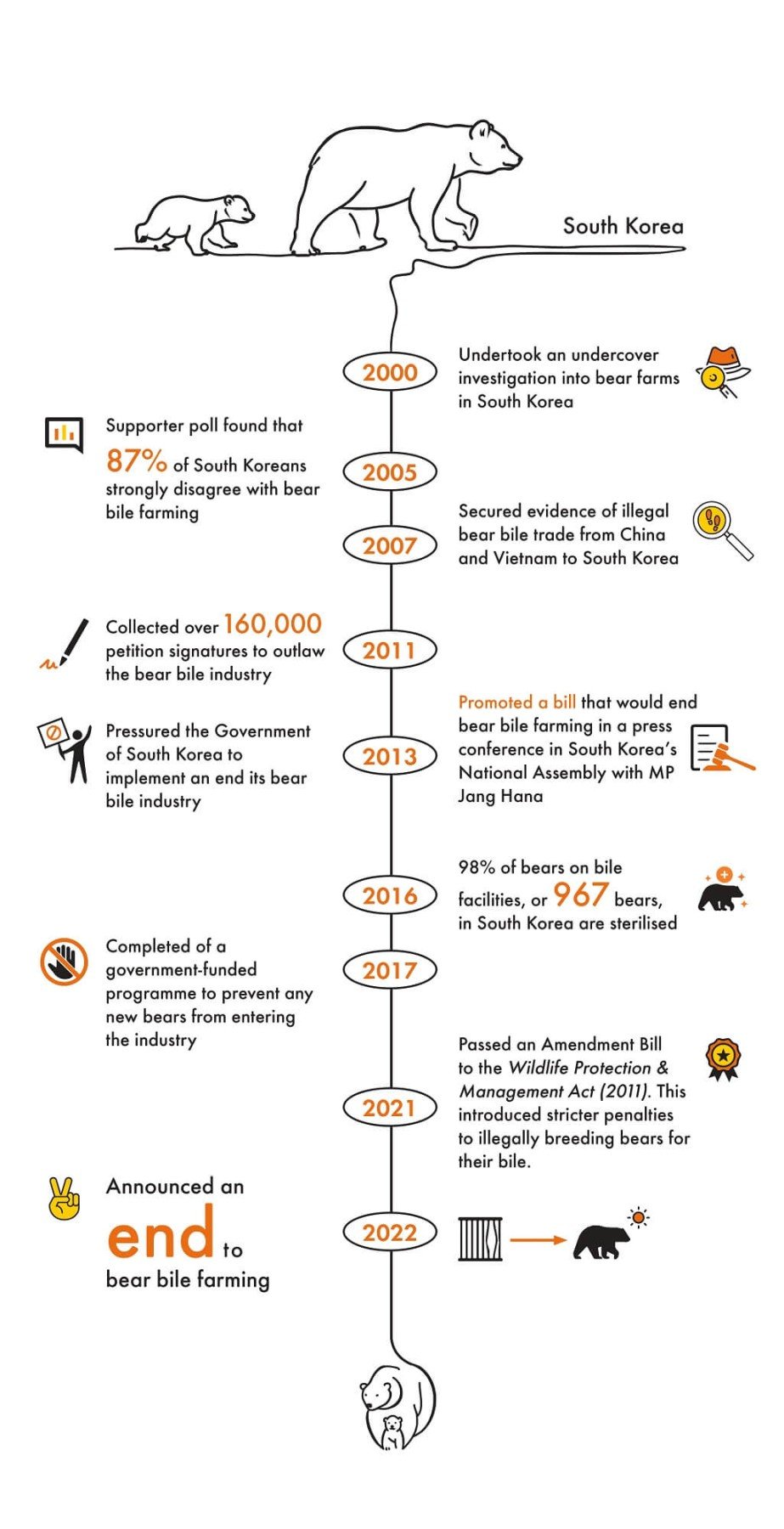
Together, with our supporters’ help, we can create lasting change to prevent the severe pain and psychological distress suffered by bears in the bear bile industry.
We are committed to ending the exploitation of bears in the bear bile industry, and to protect wild bears from a lifetime of suffering in captivity. Our work includes:
In 1997, World Animal Protection joined forces with the Bioresource Research Centre (BRC) in Pakistan to bring a permanent end to the tradition of using bears for entertainment. Our early partnership with BRC focused on investigative work and in more recent years on public awareness and the bear sanctuary.
The key message we are communicating to key decision makers and bear owners, is that the practice of keeping bears for entertainment is cruel, culturally unacceptable and illegal.
This campaign will eradicate the culture of using bears for entertainment by:



You can help end the cruel use of bears for human “entertainment” or as traditional medicine ingredients.
Please donate today, help ensure bears have lives worth living and help us work together to keep wild animals in the wild, where they belong.
Every year, thousands of animals are bred in captivity or snatched from the wild to be brutally killed for their body parts.
Your support can help to cover food and medical costs that protect bears at our partner sanctuaries.
We worked in Romania to free bears that are being kept in captivity – often in tiny, barren, concrete cages – by private owners and zoos.

Join thousands of animal lovers fighting to protect wildlife and give farmed animals good lives. Sign up now to receive emails with all the ways you can help.
Sign up